| You are here: Home: BCU 4|2002: Program Supplement: Local and Systemic Therapy of DCIS
| Local
and Systemic Therapy of DCIS |
|
| Surgeons: What percent of your
DCIS patients do you treat with the following:

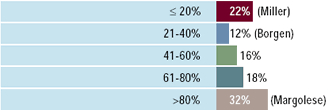
Miami meeting attendees: What fraction of your
patients with DCIS receives tamoxifen?
|
|
Most patients with DCIS are being treated with lumpectomy and radiation
as local therapy. While there is considerable controversy about
selection of patients for breast-conserving therapy without radiation,
only about one in seven women receive this local treatment approach.
There is significant variation in the use of tamoxifen for DCIS
patients. Although NSABP B-24 demonstrated approximately a 50% reduction
in the rates of all breast cancer events with the use of tamoxifen
in DCIS patients, some physicians believe the potential toxicities
outweigh the absolute benefits of therapy in many patients with
this low-risk lesion.
Bordeleau L et al. A comparison of four treatment strategies
for ductal carcinoma in situ using decision analysis. Cancer
2001;92(1):23-9. Abstract
Fisher B et al. Prevention of invasive breast cancer in women
with ductal carcinoma in situ: An update of the National Surgical
Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project experience. Semin Oncol
2001; 28(4): 400-18. Abstract
Mirza NQ et al. Ductal carcinoma-in-situ: Long-term results
of breast-conserving therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2000;7(9):656-64.
Abstract
Skinner KA, Silverstein MJ. The management of ductal carcinoma
in situ of the breast. Endocr Relat Cancer 2001;8(1):33-45.
Full-text
Winchester DP et al. The diagnosis and management of ductal
carcinoma in-situ of the breast. C A Cancer J Clin 2000;50(3):184-200.
Full-text
| Implications
of the ATAC Trial in the Systemic Therapy of DCIS |
|
| Surgeons: What results would
you expect from a trial comparing tamoxifen to anastrozole
in women with DCIS?
Surgeons: Would you currently use anastrozole
or another aromatase inhibitor in a postmenopausal woman
with DCIS?

|
|
 |
 |
Based on the encouraging initial ATAC trial results with regard
to both toxicity and second breast cancers, the NSABP is planning
a randomized trial in DCIS patients comparing anastrozole to tamoxifen.
The IBIS II trial in the United Kingdom will also evaluate anastrozole
in DCIS patients. More than half of the surgeons surveyed believe
that a randomized trial comparing tamoxifen to anastrozole in women
with DCIS would yield both greater benefits and less toxicity with
anastrozole. More than half of the surgeons surveyed would currently
utilize an aromatase inhibitor based on the ATAC data, for which
there is no FDA indication. In contrast, breast cancer researchers
almost uniformly believe that aromatase inhibitors should only be
given to DCIS patients enrolled in a clinical trial.
Baum M. The ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination)
adjuvant breast cancer trial in post-menopausal women. Breast
Cancer Res Treat 2001;69(3): Abstract
8.
Chlebowski RT. Breast cancer risk reduction: Strategies for
women at increased risk. Annu Rev Med 2002;53:519-40.
Abstract
Fabian CJ, Kimler BF. Beyond tamoxifen: New endpoints for breast
cancer chemoprevention, new drugs for breast cancer prevention.
Ann NY Acad Sci 2001;952:44-59. Abstract
O’Regan RM, Jordan VC. Tamoxifen to raloxifene and beyond.
Semin Oncol 2001;28(3):260-73. Abstract
Powles TJ. Breast cancer prevention. Oncologist
2002;7(1):60-4. Abstract
|
