|
|
||||||||||||||
![]()
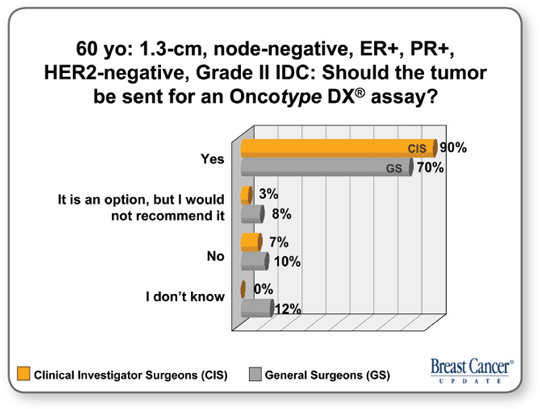

FACULTY COMMENTS
![]() DR RAVDIN: During the past two years, the issue of smaller, ER-positive,
HER2-negative, node-negative tumors has become an
area of contention and enormous expectation. Ordinarily, these
patients with ER-positive disease would most likely receive endocrine
therapy, but the question is, would they benefit from chemotherapy in
addition to hormone therapy? The idea is that we’ll be able to identify
patients who will obtain a particularly low degree of benefit from
chemotherapy and be able to prevent overtreatment. The hope is that
we will revolutionize treatment for patients with ER-positive disease
who are at low risk.
DR RAVDIN: During the past two years, the issue of smaller, ER-positive,
HER2-negative, node-negative tumors has become an
area of contention and enormous expectation. Ordinarily, these
patients with ER-positive disease would most likely receive endocrine
therapy, but the question is, would they benefit from chemotherapy in
addition to hormone therapy? The idea is that we’ll be able to identify
patients who will obtain a particularly low degree of benefit from
chemotherapy and be able to prevent overtreatment. The hope is that
we will revolutionize treatment for patients with ER-positive disease
who are at low risk.
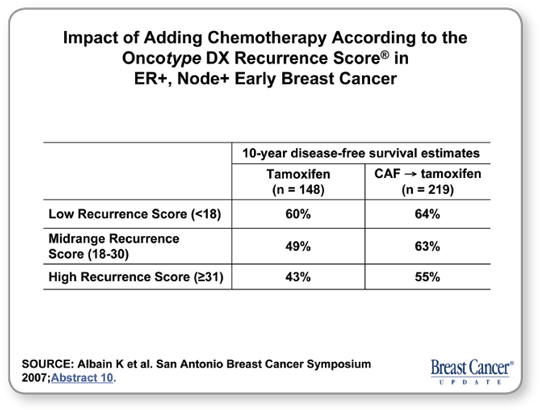
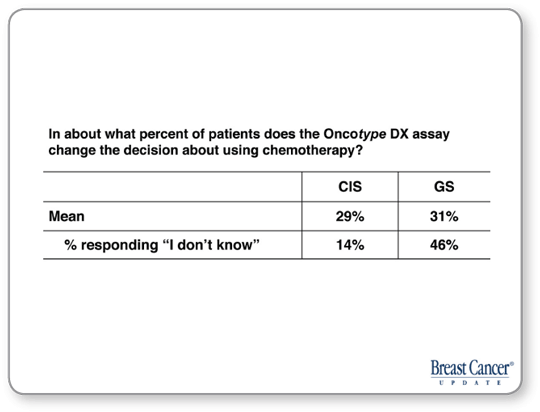
One line of thought is that molecular markers will allow us to use the multigene assays as in the NSABP-B-20 study, which demonstrated that patients with low Oncotype Recurrence Scores did not benefit from chemotherapy. More recently, SWOG presented a node-positive trial at San Antonio evaluating patients who received tamoxifen and were then randomly assigned to chemotherapy or not. Again, the low-risk molecular signature identified patients who obtained no risk reduction from chemotherapy.
| Table of Contents | Top of Page |
Editor's Note
State of the art 2008
Neil Love, MD
Slides and Faculty Comments
Sentinel Lymph Node Biospy (LSNB) Relative to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy
Sentinel Node Biopsy Injection Site
Partial Breast Irradiation (PBI)
Genomic Assays: Prediction of Benefit from Chemotherapy
Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
A CME Audio Series and Activity