| You
are here: Home: Web
Guide 02- Surgeons: Armando
E Giuliano, MD

Edited comments by Dr Giuliano
ACOSOG-Z0010 trial: Enhanced sentinel node pathology
and iliac crest bone marrow aspiration in patients with negative
sentinel nodes
ACOSOG-Z0010 is a prospective observational trial designed to
determine the clinical significance of sentinel node and bone marrow
micrometastases. A number of studies show that bone marrow micrometastases
have the same adverse implications as lymph node micrometastases.
A patient with negative lymph nodes but positive bone marrow will
have a similar outcome as a patient with lymph node metastases.
Interestingly, bone marrow metastasis appears to be an independent
prognostic factor, indicating a different metastatic pathway. While
lymph node metastases have a lymphatic pathway, bone marrow metastases
may have more of a direct systemic pathway.
We may be able to more accurately differentiate high-risk versus
low-risk patients by combining lymph node and bone marrow examination.
Perhaps patients with both negative bone marrow and a negative lymph
node by immunohistochemistry have a very low risk of metastatic
disease and don’t need adjuvant therapy. Z0010 will tell us
so much more about the biology of breast cancer and may cause us
to re-examine how we treat especially those patients with node-negative
disease.
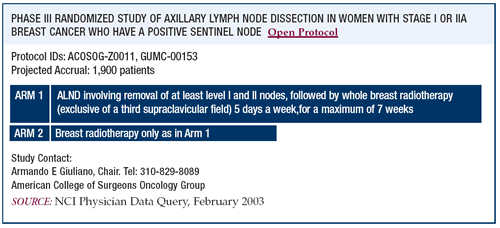
ACOSOG-Z0011 trial: Axillary dissection versus
observation
The ACOSOG-Z0011 trial is a very important trial because we’ve
being doing axillary dissection for over 100 years, and we are still
uncertain of its survival benefit. NSABP B-04 is a classic breast
cancer study, and even with 26 years of follow-up, there is no survival
difference between patients who had immediate dissection and those
who did not have axillary dissection unless they had an axillary
recurrence.
Z0011 examines the role of axillary dissection in node-positive
patients. It’s hard to imagine that removing 20 lymph nodes
is of value in a node-negative patient, so we are looking only at
the node-positive patients. In essence we’re doing a “high-tech
NSABP B-04.”
Patients with H&E metastases are randomized to axillary dissection
or no axillary dissection and no axillary radiation. Patients are
treated with adjuvant systemic therapy, as indicated. This is a
very difficult randomization for physicians and patients to accept.
The study has been open for about three years and we’ve accrued
400 out of our target of 1,800 patients.

NSABP B-32 trial of axillary dissection versus
no further axillary surgery
NSABP B-32 has a different design than the American College of
Surgeons' trials. Patients whose sentinel node is negative are randomized
to axillary dissection or no axillary dissection. The study will
confirm the accuracy of SLNB and evaluate the clinical recurrence
rate and overall survival in a randomized setting. They will also
try to determine the prognostic significance of IHC-detected micrometastases.
It's an important trial that has accrued approximately 3,500 patients.
Clinical use of endocrine therapy by surgeons
Some surgeons prescribe their own hormonal manipulation, and those
physicians will continue to do so as aromatase inhibitors are introduced
into practice. Many patients have a fear of tamoxifen. Some women
with high-risk breast cancer say, "I don’t want to take
tamoxifen — it causes cancer." Patients often complain
about hot flashes, which affect their quality of life. They also
express concerns about endometrial cancer, deep vein thrombosis
and even weight gain. Once you start to weigh the risks and rewards
there's no question tamoxifen is of tremendous value; however, a
drug with fewer side effects would be more tolerable to patients.
Anastrozole has fewer side effects and is at least as effective
as tamoxifen — it is very easy to use.
Select publications
|
