|
 Home:
Meeting
Highlights: Posters
Home:
Meeting
Highlights: Posters

Ductal
Lavage and Detection of Abnormal Cytology in Women at High Risk
for Breast Cancer
William Dooley, Umberto Veronesi, Richard Elledge, Joyce O’Shaughnessy,
Susan Love, Britt Marie Ljung and the Ductal Lavage Investigators
| Introduction
and Background |
Breast
cancer originates in the milk ducts. Ductal fluid cytology is routinely
used clinically to evaluate spontaneous nipple discharge. Cytology
from nipple aspirate fluid (NAF) has also been used in the research
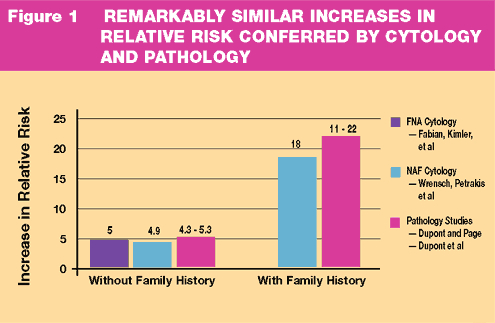
setting. Wrensch and Petrakis, et al., have reported on 2,300 women
followed for 12.7 years with cytology on NAF. Women with cellular
atypia had a 4.9-fold increase in the relative risk of developing
breast cancer. The increase in relative risk was 18-fold in women
with cellular atypia and a positive family history. Fabian, et al.,
reported a 5.0-fold increase in relative risk in a high-risk cohort
of women with hyperplasia with atypical cells obtained by random
fine needle aspiration. Similar increases in risk are conferred
by atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) in studies by Dupont and Page.
- To determine
the safety and feasibility of ductal lavage using a microcatheter
in women at high risk for breast cancer.
- To determine
the relative sensitivity of nipple aspiration and ductal lavage.
Subjects underwent nipple aspiration followed by ductal lavage of
all fluid-yielding ducts. Women who did not have NAF did not undergo
ductal lavage.

|
ASPIRATION
|
CANNULATION
OF DUCT
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Gentle
suction is applied to the nipple to elicit fluid. |
2.
|
Microcatheter is inserted into duct. |
|
INFUSION
|
MASSAGE
OF BREAST
|
|
|
|
|
3.
|
10-20
mL of saline is slowly introducedinto the milk duct in 2 - 4
mL increments to lavage the duct and collect epithelial cells. |
4.
|
The
breast is massaged to bring fluid forward. |
- NAF obtained
in 84% of subjects
- Average of
1.5 NAF-yielding ducts/breast
- 417 subjects
had samples sent for NAF cytology n 383 subjects had samples sent
from 591 ducts for ductal lavage cytology
- 92% of subjects
had at least one attempted duct successfully cannulated n There
were no procedure-related serious adverse events
- Two local
infections were treated with oral antibiotics
- Median subject
rating of procedure discomfort was 24 with 0 representing no pain
and 100 severe pain
| Abnormal
Cytology Results |
|
DUCTAL
LAVAGE SAMPLE
|
|
Ductal
lavage obtained, on average, 40,000 epithelial cells per duct.
78% of samples were adequate for diagnosis. In comparison, NAF
samples had ~1,800 epithelial cells per breast and only 27%
were adequate. |
 |
|
BENIGN
|
MILDLY
ATYPICAL
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUSPICIOUS
(MARKEDLY ATYPICAL)
|
MALIGNANT
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Abnormal
cells were detected in a total of 24% of subjects.
- Atypical:
17% (66/383 subjects) n Suspicious/Malignant: 7% (26/383 subjects)

Occult DCIS
detected in 4/11 surgical workups:
- Sizes: 1.8
cm, 6 cm and <2 mm
- Grade range:
high to intermediate grade Surgical Findings to Date:
- 4 cases of
DCIS
- 5 cases of
papillomatosis and/or ADH
3 cases
by ductoscopy-guided excisional biopsy
1 case
by dut excision
1 case
by mastecto
- 2 cases of
fibrocystic changes
Issues
- Over-reading
of cytology?
- Incomplete
surgical resection?
- Incomplete
histopathology?
Case Study: Subject CW
- 29 y.o. with
previous cancer/mastectomy in R breast; underwent ductal lavage
in L breast
- Suspected
malignant cells in one duct in L breast
- Negative
mammogram and ductogram after lavage
- Lymphazurin
infused down suspicious duct and exploration/resection of "blue"
ducts performed
|
|
|
|
Suspicious
for Malignancy
|
Extensive
DCIS, intermediate grade,
6.0 cm (greatest dimension)
|
- 62 y.o. woman,
Gail 2.9 with 4 negative mammograms prior to lavage
- First lavage
8/99: malignant cells in a single duct in one breast
Negative
mammogram and ductogram (high mag) after lavage
- Second lavage
10/99: Suspicious duct cannulated; malignant cytology confirmed
- Third lavage
and surgery 11/99: Suspicious duct cannulated; lymphazurin injected
down duct and "blue" ductal system resected
Pathology
Results:
- High grade
DCIS with focal comedo necrosis
- 1.8 cm in
estimated size involving large lactiferous ducts extending to
2 mm from inked margins
|
CYTOLOGY
|
PATHOLOGY
|
|
|
 |
- Ductal lavage
is a safe, well-tolerated and minimally invasive procedure for
collecting breast ductal epithelial cells for the determination
and differentiation of normal, premalignant and malignant cells.
- Ductal lavage
collects ductal epithelial cells far more efficiently than nipple
aspiration and is more sensitive than nipple aspiration for detecting
cellular abnormalities in the breast.
- Ductal lavage
may be a useful adjunct to mammography and other currently available
imaging modalities for the early detection of intraductal breast
pathology.
Ductal Lavage
Investigators:
- W. Dooley,
Johns Hopkins
- U. Veronesi,
Istituto Europeo di Oncologia
- R. Elledge,
Baylor/Houston
- J. O'Shaughnessy,
Baylor/Dallas
- H. Kuerer,
MD Anderson
- S. Khan,
SUNY – Syracuse
- D. Hung,
Pro•Duct Health
- R. Phillips,
Atlanta
- P. Ganz,
UCLA
- D. Euhus,
U. Texas, SW
- L. Esserman,
UCSF
- B. Haffty,
Yale
- M. Kelley,
Vanderbilt
- M. Anderson,
King/Drew
- P. Schmit,
UCLA/Olive View
- R. Clark,
Santa Barbara
- B. Anderson,
U. Washington
- S. Troyan,
Beth Israel Deaconess
- R. Arias,
USC
Top
of Page
|



